The Role of Protein in Low-Carb Diets for Muscle Repair
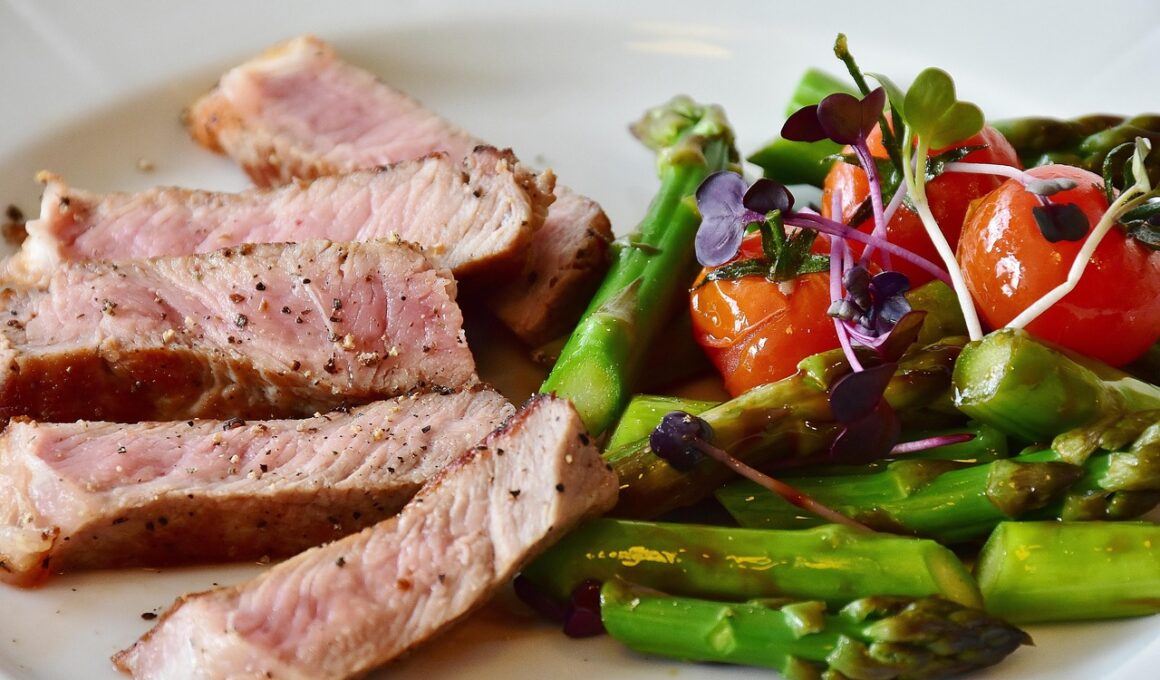
Low-carb diets have gained tremendous popularity, primarily for their effectiveness in weight management and health improvement. Within these diets, protein plays a crucial role in muscle repair, recovery, and growth. When you follow a low-carb diet, it typically involves reducing sugar and starch intake while emphasizing lean protein and healthy fats. This dietary change significantly alters the body’s energy source, utilizing fat for fuel instead of carbohydrates. The amino acids found in protein contribute to muscle synthesis, which can be particularly important during periods of calorie deficit. However, understanding how much protein to include in your diet is key to maximizing its benefits without compromising muscle mass. Additionally, high-protein foods designed for muscle recovery support can enhance athletic performance. Opting for lean meats, fish, eggs, dairy, and protein supplements are effective strategies to ensure an adequate intake. Therefore, focusing on protein allows individuals following low-carb diets to maintain strength, enhance recovery, and achieve their fitness goals efficiently. Overall, balancing protein intake with lower carbohydrate levels can significantly impact muscle health and overall well-being.
Understanding Protein’s Role
Protein serves many functions in the body, particularly when adhering to a low-carb diet that promotes muscle repair. This macronutrient is necessary for building and repairing tissues, especially after exercise. Muscles sustain stress during strength training and need sufficient protein to recover adequately. A well-planned low-carb diet incorporates quality protein sources to facilitate muscle repair and growth. A diet higher in protein may also help maintain satiety and reduce cravings, which assists in controlling overall caloric intake. In this way, protein functions not only as a building block but also as a strategic nutrient in managing dietary habits. Common sources of protein include chicken, beef, fish, tofu, and legumes. It’s vital to choose options that align with your nutritional preferences and restrictions. Furthermore, distributing protein intake evenly across meals may optimize muscle protein synthesis throughout the day. Adequate hydration and micronutrient intake should also be considered when enhancing muscle recovery. Protein quantity can vary based on activity levels, age, and individual goals. Thus, tailoring your protein needs while on a low-carb diet can provide essential support for maintaining and growing muscle.
When engaging in a low-carb diet, determining the appropriate amount of protein is crucial to maximize health benefits. Generally, experts recommend consuming around 1.6 to 2.2 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight, particularly for those aiming to enhance muscle mass or recovery. Individuals participating in regular strength training or intense exercise may require more protein to meet their body’s demands. Adapting your protein intake based on activity level can ensure adequate muscle repair and growth. Additionally, nutritionists emphasize spreading protein consumption throughout the day to promote consistent muscle protein synthesis. Balancing macronutrient distribution effectively sets the stage for successful recovery. Lean meats, seafood, dairy products, eggs, and plant-based protein sources should comprise your protein intake. These foods not only supply adequate protein but also contain essential vitamins and minerals that support overall health. It’s essential to prioritize whole food sources whenever possible. Monitoring protein intake and adjusting it according to physical activity intensity and nutritional goals can lead to better outcomes. Ultimately, proper nutritional planning can make a significant difference in performance and recovery for those following a low-carb approach.
Sourcing Quality Protein
Sourcing quality protein is vital when following a low-carb diet since muscle repair and growth depend significantly on the nutrients consumed. To achieve this, consider integrating a variety of protein-rich foods into your nutrition plan. Aside from common sources like chicken, turkey, and fish, incorporating plant-based proteins such as quinoa, lentils, and chickpeas can also provide beneficial nutrients while ensuring diversity within meals. Dairy products like Greek yogurt and cottage cheese can serve as excellent snacks due to their high protein contents. Additionally, protein powders can serve as convenient supplements for individuals struggling to meet protein requirements through food alone. Furthermore, when seeking animal-based sources, selecting grass-fed options whenever possible can improve the nutrient profile. It’s crucial to remember that not all protein sources are created equal, so including a spectrum of nutrient-dense foods will provide necessary amino acids. Before making significant dietary changes, consulting with a nutritionist may offer tailored guidance in meeting specific protein needs. Adequate sourcing will lead to better muscle recovery, enhancing the overall success of a low-carb diet approach.
Besides quantity and variety, timing nutrient intake can also play a significant role in muscle recovery for individuals on low-carb diets. Post-workout nutrition is often cited as the most crucial time for protein synthesis, and consuming protein-rich meals or snacks soon after exercise may optimize recovery. Having a family of carbohydrates may not be essential for recovery, but coupling protein with moderate carbs can enhance overall recovery and replenishment. Additionally, many fitness practitioners recommend a protein-rich breakfast, as starting the day with high-quality protein can improve satiety while supporting muscle preservation. Incorporating a mix of healthy fats such as avocados, nuts, and olives can provide balanced meals that fuel the body for workouts while supplementing protein. Distributing protein intake across meals can ensure muscles continually receive the nourishment they need for recovery. Regular assessments of progress and adjustments to dietary strategies can enhance the effectiveness of a low-carb approach. Listening to your body’s signals regarding hunger and recovery can also improve dietary adherence and overall well-being. This equilibrium allows for sustainable muscle health and fitness outcomes.
Challenges and Solutions
Despite the numerous benefits of protein in low-carb diets, challenges might arise in obtaining sufficient nutrition to support muscle repair. For example, some individuals may experience difficulty adjusting to reduced carbohydrate intake and find themselves craving starches or sugars. Developing effective meal preparation strategies can mitigate these urges. Planning meals in advance can ensure varied protein sources are available and address hunger consistently. Additionally, staying informed about the nutritional content of foods and making conscious decisions can support healthy eating habits. Encouraging experimentation with different cooking methods or recipes can help maintain interest and excitement around meal times. Trying new proteins, seasoning techniques, and meal preparation styles can contribute to dietary enjoyment while remaining on track. Consulting with registered dietitians can provide personalized strategies to optimize protein intake on a low-carb diet. Tailoring individual preferences can facilitate compliance, allowing for smoother transitions into this way of eating. Focusing on gradual adjustments can lead to successful long-term adherence to low-carb dietary practices.
In conclusion, the role of protein in low-carb diets is vital for maintaining muscle health and ensuring effective muscle repair. Prioritizing high-quality protein sources can lead to improved performance, better recovery, and enhanced overall well-being. Understanding the significance of protein quantity, timing, and digestion will help individuals make informed choices to maximize their dietary benefits. Keeping protein-rich foods accessible and varied is key to preventing diet fatigue. Moreover, being in tune with one’s body can help to reinforce the importance of nutritional choices. For those engaged in regular exercise or strength training, protein plays a unique role in achieving fitness objectives while adhering to low-carb lifestyle principles. This balance of dietary practices can support muscle growth, improve performance, and sustain energy levels throughout the day. Individuals can create a nutritionally rich plan that aligns with their goals by empowering themselves with knowledge and resources. Ultimately, following a well-structured low-carb diet that emphasizes protein will significantly influence performance and muscle repair, leading to a healthier and more fulfilling lifestyle.