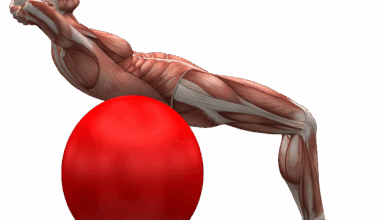
Using Isometric Exercises in Rehabilitation and Strength Training
Isometric exercises play a significant role in both rehabilitation and strength training regimes. Practicing isometric movements can aid in muscle stabilization and joint protection, making them an essential tool for recovery from injuries. These exercises involve voluntary muscle contractions without changing muscle length. A popular example includes holding a plank position, which engages multiple muscle groups and enhances core stability. One of the key advantages of isometric exercises is their capability to enhance muscle endurance and strength without unnecessary strain on damaged tissues. Those recovering from injury often face restrictions that limit their ability to perform traditional movements. Isometric workouts present a low-risk way to build strength while ensuring safety and stability. Additionally, they are particularly beneficial in fostering neural adaptations, priming the muscles for future dynamic exercises. This leads to improved functional performance over time, which is essential for athletes and active individuals. Incorporating isometric exercises effectively into rehabilitation protocols allows faster return to regular movement patterns. Physical therapists often recommend these workouts for patients in different stages of recovery, facilitating a tailored approach to rehabilitation.
Benefits of Isometric Exercises
One of the foremost benefits of isometric exercises is their simplicity and versatility. They can be performed nearly anywhere, requiring minimal equipment and space. This characteristic makes them accessible for individuals undergoing rehabilitation who may have mobility or range-of-motion restrictions. Additionally, they are easy to modify, allowing practitioners to adjust the intensity according to the individual’s progress. Isometric exercises effectively target specific muscle groups, enabling individuals to strengthen areas of weakness without aggravating pre-existing injuries or irritations. Importantly, these exercises are known to improve muscle coordination, stability, and proprioception, which are crucial for injury prevention. Another noteworthy advantage is that isometric exercises can promote the maintenance of muscle mass during periods of inactivity or recovery. By focusing on activating the muscles without excessive loading, individuals can minimize muscle atrophy while gradually regaining strength within their recovery framework. Several sports professionals incorporate isometric exercises into their training regimens as supplementary work. They acknowledge the relevance of these exercises in developing total body strength and enhancing performance metrics, making them favorable for athletes aiming to maximize resilience.
Isometric exercises also provide an excellent alternative for individuals who might experience pain during traditional dynamic movements. This is especially pertinent for those with joint problems or postoperative recovery plans. Pain management often dictates the modalities of rehabilitation protocols, and isometric training can help bridge the gap between initial rehabilitation phases and progressive activity regimens. Moreover, with consistent practice, patients often report increased self-confidence and enthusiasm regarding their rehabilitation journey. The mental aspect of engaging in a structured yet adaptable training routine cannot be overstated. Developing a positive mindset during recovery is crucial as it can influence overall motivation and adherence to rehabilitation. Isometric exercises allow individuals to feel empowered by their ability to engage with their recovery process actively. A skilled physical therapist can help create a routine that incorporates various isometric exercises while gradually increasing intensity and complexity over time. This assists in ensuring that individuals remain challenged and engaged throughout their rehabilitation experience. As progress continues, these exercises can be seamlessly integrated into broader strength training routines, creating a holistic framework for effective rehabilitation strategies.
Integrating Isometric Exercises into Training
When considering effective integration of isometric exercises into rehabilitation and strength training, clear structure is paramount. Typically, practitioners might begin with a foundation of core isometric holds, complemented by muscle isolation exercises to ensure proper muscle activation. Working on stabilizing muscles before engaging larger muscle groups can help create a solid base of support essential for dynamic movements later. Incorporating isometric holds at various angles of joint flexion enhances muscular development and increases functional strength. Training programs that blend isometric holds with dynamic movements allow individuals to reap benefits from both modalities. Transitioning between positions and varying the duration of isometric contractions can lead to progressive overload, which is crucial for ongoing strength improvements. Additionally, engaging in isometric exercises before or after dynamic workouts enhances overall muscle performance, as it promotes muscle awareness and activation. These adjustments help ensure optimal engagement during traditional exercises. Finally, professionals should continuously assess patients’ responsiveness to ensure modifications align with their evolving capabilities and goals. This approach not only promotes continuous improvement but also maximizes safety and effectiveness during rehabilitation and strength training.
Progress tracking and goal setting are equally critical components to consider when integrating isometric exercises into a training regimen. Clients should communicate their specific objectives, such as enhancing muscle endurance or transitioning back to sports activities. Establishing clear milestones not only fosters motivation but also provides a framework for measuring progress throughout the rehabilitation journey. A combination of subjective feedback from clients regarding their comfort or perceived exertion, along with objective data like strength measurements or improved range of motion, ought to guide adjustments in their program. This dual approach allows trainers or therapists to shape their strategies according to the unique needs of each individual. Regular communication regarding their improvement can serve to bolster client satisfaction and commitment to rehabilitation protocols. Including isometric elements in gym settings encourages social interaction and teamwork, which are essential for many clients recovering from injuries. With progress assessments, individuals who experience enhanced performance can also share experiences that cultivate camaraderie among peers. All of these factors contribute to developing a well-rounded training environment tailored to promoting recovery and strength training effectively.
Considerations and Safety Precautions
While isometric exercises offer various benefits in rehabilitation and strength training, several important safety precautions must be observed. Thoroughly assessing clients’ medical histories and understanding potential limitations is essential. Individuals with high blood pressure or cardiovascular concerns need to approach isometric training with particular attention to exertion levels and breathing techniques. As isometric exercises can lead to significant muscular tension, proper alignment and technique are crucial to avoid overexertion or strain. Therefore, it is advisable to instruct clients on maintaining proper posture throughout each hold to ensure safety and efficacy. Progress should occur gradually; beginners may start with shorter durations of maintaining isometric holds, allowing adequate recovery time between sets. This approach fosters optimal muscular adaptation while safeguarding against injury risks. For advanced clients, intermittent isometric intervals addition to dynamic kettlebell or resistance activities may provide the complexity needed to enhance performance. Moreover, practitioners should closely monitor individuals’ responses during these exercises, adjusting plans based on their feedback and progress. This ongoing assessment offers reassurance to both clients and professionals, reinforcing the importance of prioritizing safety in all rehabilitation and strength training endeavors.
In conclusion, isometric exercises represent a powerful tool in the domains of rehabilitation and strength training. Their versatility, simplicity, and efficacy make them a favorable choice for individuals recovering from injuries, as well as athletes aiming to improve their performance levels. By focusing on muscle activation while minimizing joint stress, isometric exercises facilitate a safe environment for strength enhancement. Practitioners should remain attuned to the individual needs of clients, ensuring that proper technique is emphasized and safety measures are consistently maintained. The successful integration of isometric exercises within comprehensive rehabilitation plans can expedite recovery while reinforcing stability and strength. With careful consideration and informed progression, individuals can make significant strides toward regaining mobility, achieving muscle endurance, and enhancing overall physical confidence. Furthermore, fostering communication and goal setting deepens engagement in the recovery process, promoting adherence to prescribed programs. As research continues, the value of isometric training within athletic performance and rehabilitation will likely become increasingly recognized. Ultimately, professionals working within these fields can leverage the potential of isometric exercises to create impactful and empowering training experiences for diverse populations.