Shoulder Ligament Injuries in Sports: Causes and Treatments
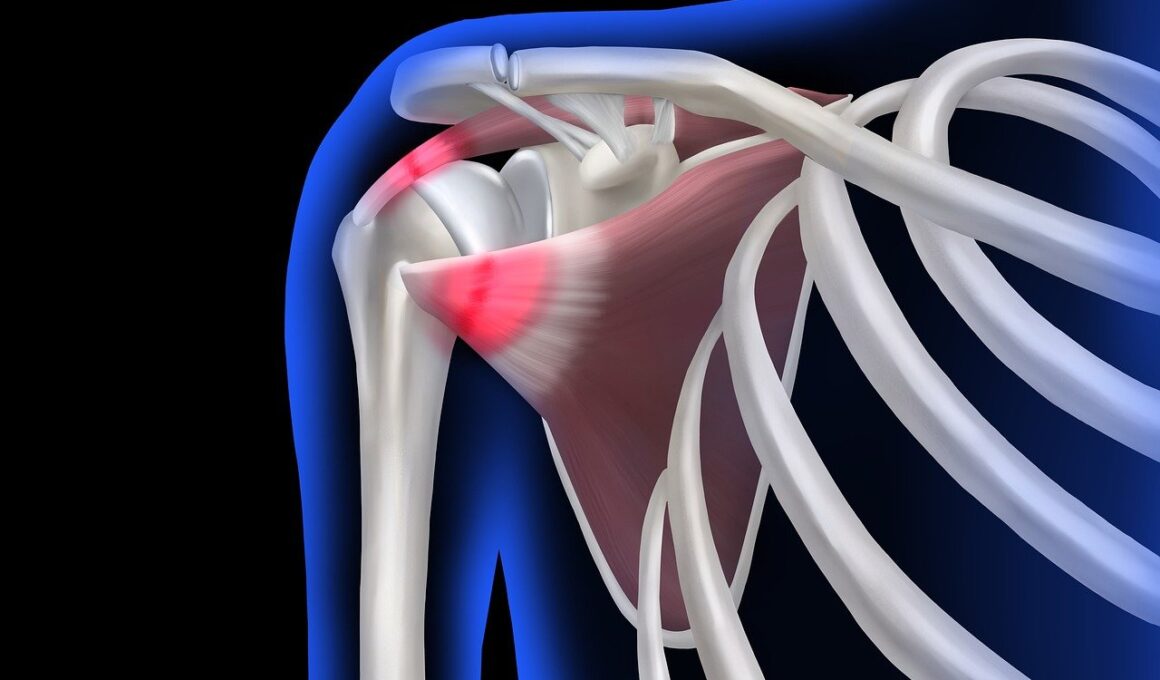
Shoulder ligament injuries are prevalent among athletes, particularly those engaged in sports that demand overhand motion, such as baseball, tennis, and swimming. These injuries can occur as a result of acute trauma or repetitive strain. Acute injuries might happen during a fall or a sudden impact, while chronic injuries often develop over time due to wear and tear on the ligaments. Understanding the anatomy of the shoulder is crucial, as the network of ligaments provides stability. The primary ligaments involved in shoulder injuries include the acromioclavicular (AC) joint ligaments and the glenohumeral ligaments. Damage to these structures can alter an athlete’s performance significantly and lead to extended recovery time if not treated properly. For athletes, identifying the type and extent of the ligament injury is essential to determining the appropriate treatment. A thorough medical examination typically includes physical evaluations, imaging techniques, and assessments of functional limitations. If not addressed, ligament injuries can lead to chronic pain, instability, and potential long-term consequences, including degenerative joint issues, which must be taken seriously to ensure a successful return to sport.
Common Causes of Shoulder Ligament Injuries
Several factors contribute to shoulder ligament injuries among athletes. First, overuse is a significant aspect, especially in sports requiring repetitive motions, such as tennis. Continuous stress on the ligaments can lead to microtears, creating chronic pain and instability. Second, poor biomechanics can increase the risk of injury. Athletes who lack proper technique or strength may place excessive strain on their shoulder ligaments during activity. This is especially prominent in sports such as football and wrestling, where falls and quick directional changes are frequent. Third, a lack of flexibility contributes to these injuries as tight muscles surrounding the shoulder can create imbalances and put stress on ligaments. Strength and conditioning play a vital role in preempting injuries as well; athletes with insufficient muscle strength may not provide enough support for their shoulder joints. Additionally, a history of previous injuries can predispose athletes to re-injury. Preventative measures, including strength training, stretching, and technique improvement can significantly decrease the risk of shoulder ligament injuries in athletes.
Diagnosing shoulder ligament injuries necessitates detailed assessment due to the intricate anatomy of the shoulder. A medical professional typically begins with a comprehensive review of the athlete’s symptoms and physical activities. Interestingly, Pain in the shoulder, loss of range of motion, and instability are frequent indicators of ligament damage. In addition, specific tests, including the apprehension test and the relocation test, can be utilized to assess the integrity of the ligaments. Imaging techniques, such as MRI and ultrasound, provide crucial information regarding the extent of the damage, revealing whether there are tears or inflammation in the ligaments. The results from these diagnostic approaches guide treatment options. In acute cases with complete tears, surgical intervention may be warranted. Conversely, partial tears or chronic injuries could respond to conservative measures such as physical therapy, medications, and lifestyle adjustments. Understanding the scope of the injury is vital in developing a personalized rehabilitation program aimed at restoring function and preventing future injuries. This comprehensive approach puts athletes on the path to recovery and helps enhance their future performance.
Treatment Options for Shoulder Ligament Injuries
There are various treatment approaches for shoulder ligament injuries, and the choice largely depends on the severity of the injury. In mild cases, conservative management typically includes rest, ice application, and over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medications. This non-invasive approach allows the body to heal naturally. Additionally, physical therapy is essential in rehabilitation to strengthen muscles surrounding the shoulder and restore range of motion. As the recovery progresses, exercises focusing on stability and flexibility ensure a comprehensive return to sport. For more severe injuries, surgical options, such as arthroscopy, may be considered. Arthroscopy allows for minimal invasiveness to repair or reconstruct torn ligaments. Following surgery, rehabilitation remains crucial for regaining strength and preventing stiffness. The timeline for recovery can vary, with more significant injuries requiring months of rehabilitation. Patience and adherence to rehabilitation protocols are imperative for athletes to ensure a secure return to competition. Open communication between the athlete, medical team, and coaches is necessary to manage expectations and achieve recovery goals effectively.
Preventing shoulder ligament injuries is a priority for athletes and coaches alike. Several strategies can aid in reducing the risk of injuries effectively. Firstly, developing a well-rounded strength and conditioning program helps fortify the shoulder girdle, emphasizing the rotator cuff muscles and scapular stabilizers. Incorporating exercises targeting both dynamic and static stability is critical to enhance overall shoulder function. Secondly, proper warm-up routines and flexibility training are essential to preparing muscles, tendons, and ligaments for the physical demands of training and competition. Furthermore, coaching proper techniques to ensure biomechanical efficiency during sports activities can reduce the excessive loading of shoulder ligaments. Lastly, athletes should always listen to their bodies and address any symptoms promptly. Ignoring pain and discomfort can exacerbate minor injuries until they become more severe. Regular monitoring and assessments feel vital to ensuring athletes maintain optimal shoulder health. In summary, a multi-faceted approach to prevention can significantly mitigate the risk of shoulder ligament injuries. Collaboration among athletes, coaches, and healthcare providers is critical to achieving better outcomes and prolonging athletic careers.
The Role of Rehabilitation in Recovery
Rehabilitation plays an integral role in the recovery from shoulder ligament injuries. A well-structured rehabilitation program aims to restore mobility, strength, endurance, and the overall functionality of the shoulder. The process begins with initial assessments to identify limitations and establish performance goals going forward. Depending on the injury severity, rehabilitation starts with passive range-of-motion exercises before progressing to active movements. It’s crucial to introduce these stages at a pace suitable for the athlete’s healing process. As patients become more comfortable, gradually incorporating strength training, resistance exercises, and sport-specific drills will facilitate a safe return to normal activities. Communication between the athlete and rehabilitation specialists influences the flexibility and adaptability of the regimen. Moreover, rehabilitation must also address psychological recovery, as injuries may instill fear and uncertainty in athletes. Psychological support may include counseling or mental training strategies to boost an athlete’s confidence and resilience as they transition back into competition. The continuous assessment allows for a tailored plan that enhances recovery while minimizing the risk of recurrent injuries. Thus, comprehensive rehabilitation is a vital foundation for returning to sports post-injury.
The prognosis for shoulder ligament injuries varies depending on the type and extent of the injury. Generally, soft tissue injuries like sprains can see improvements with conservative management, allowing most athletes to return to their usual activities within weeks. However, full recovery from severe injuries, including ligament tears, often requires a longer time frame, particularly if surgical interventions are involved. Factors influencing recovery include the athlete’s age, overall health, and commitment to rehabilitation protocols. Younger athletes may enjoy more favorable outcomes due to their body’s ability to heal rapidly. Conversely, older athletes may experience prolonged healing periods, which may lead to lingering issues if not adequately managed. Regular follow-ups with medical professionals help ensure a precise monitoring of progress and anticipate any potential complications or setbacks requiring adjustments in treatment plans. Moreover, educating athletes about the nature of their injuries helps them understand their recovery journey, thus fostering patience and adherence to protocols. Promoting healthy lifestyle choices, nutrition, and adequate rest can support overall rehabilitation outcomes, which is indispensable for a successful return to competitive sports life.