Keto Diet and Gut Health: What the Research Says
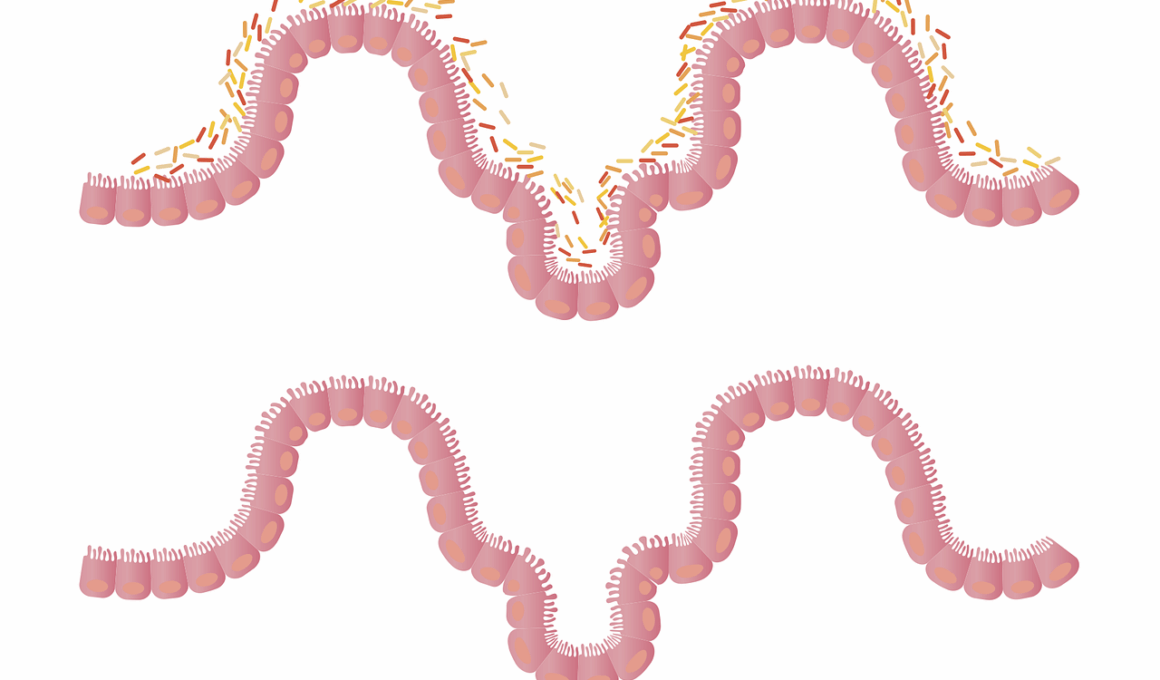
The ketogenic (keto) diet has gained popularity for its potential weight loss benefits and health advantages. However, a significant aspect worthy of consideration is its impact on gut health. The gut microbiome, comprising trillions of bacteria, plays a crucial role in digestion, metabolism, and immune function. Research indicates that dietary choices significantly influence the composition of gut bacteria. The keto diet restricts carbohydrates, which may alter gut flora diversity. A study published in the journal “Cell” suggests that low-carb diets could lead to a decreased abundance of certain beneficial bacteria while promoting others. For this reason, individuals following a keto diet should be mindful of maintaining a balanced intake of nutrients and fermented foods to support gut health. Fermented foods are known to enhance gut microbiome composition, supporting digestive health. Including sources of prebiotics, like vegetables and nuts, can also help foster a thriving microbiome. It’s essential to consult healthcare professionals before making dietary changes, especially for individuals with pre-existing conditions affecting gut health and digestion.
Digestion can be significantly affected by the types of food included in a keto diet. The diet’s restriction of carbohydrates often results in reduced fiber intake, which is essential for digestive health. Fiber promotes regular bowel movements and serves as a food source for beneficial gut bacteria. Consequently, a lack of fiber may lead to constipation and gastrointestinal discomfort for those following a strict keto approach. To counteract these negative effects, it is advisable to incorporate low-carb, high-fiber foods such as chia seeds, flaxseeds, and certain leafy greens. These options can help provide the necessary fiber while adhering to carb restrictions in a keto diet. Furthermore, prioritizing hydration is crucial, as it contributes to overall digestive function. Drinking sufficient water and herbal teas can support digestive processes and alleviate issues such as bloating or constipation. Overall, individuals considering the keto diet should emphasize a holistic approach, ensuring they maintain adequate fiber intake and hydration levels to promote optimal gut health while enjoying the benefits of a ketogenic lifestyle.
Understanding the microbiome’s role
The gut microbiome serves a multitude of functions that extend beyond digestion. It is deeply involved in metabolic processes, immunity, and even mental health. Emerging research suggests that the microbiome can influence how the body responds to different diets, including the ketogenic diet. Understanding this relationship is crucial, especially as studies indicate that a healthy microbiome can enhance the positive effects of dietary restrictions. Some research has shown that ketogenic diets can lead to an increase in certain bacteria that produce short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) beneficial for gut health. SCFAs are known to have anti-inflammatory properties and may contribute to improved gut barrier function. This underscores the importance of choosing the right foods on a keto diet to maximize gut health outcomes. Additionally, individuals should remain aware of any adverse reactions their bodies might experience while transitioning to a ketogenic lifestyle. Regular monitoring can help identify which foods within the diet contribute positively or negatively to gut health, leading to tailored dietary choices that enhance overall well-being.
On the matter of ketogenic diets, considering potential gut dysbiosis is essential. Dysbiosis refers to an imbalance in the microbial community within the gut, which could lead to various health complications. Some people on keto may notice digestive disturbances or an increase in symptoms such as bloating, gas, and irregular bowel habits. This can stem from the rapid shift from a carbohydrate-rich diet to one high in fats. Moreover, these effects might be exacerbated depending on individual microbiome baseline health. Utilizing strain-specific probiotics can be beneficial for improving gut health during dietary transitions. Incorporating probiotic-rich foods like yogurt or fermented vegetables can support digestive balance and restore beneficial bacteria in the gut. Moreover, considering digestive enzymes may enhance nutrient absorption, further contributing to gut health. Individuals must approach the keto diet mindfully and be prepared to make adjustments. Personalization may involve trial and error, learning what foods a person tolerates best while still reaping the benefits of keto.
Impacts on inflammation
Another important factor in the relationship between the keto diet and gut health is the diet’s impact on inflammation. Chronic inflammation is linked to numerous health issues, including gut disorders. Certain ketogenic foods, particularly those rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as fatty fish, walnuts, and flaxseeds, have anti-inflammatory properties. This can be a significant positive for individuals dealing with digestive inflammation, easing symptoms and supporting gut healing. On the flip side, high amounts of saturated fat or processed meats may exacerbate inflammation levels in some individuals. Consequently, the quality of fats consumed in a ketogenic diet matters greatly. Focusing on sources of healthy fats and whole foods can promote better gut and overall health. Additionally, monitoring one’s response to various foods, especially fats, can allow individuals to adapt their keto diet. The interplay between diet, inflammation, and microbial health is complex; thus, individual responses can vary widely based on one’s specific circumstances.
Finally, hydration is often overlooked but plays a vital role in maintaining gut health, especially on a ketogenic diet. When switching to keto, the body tends to lose water weight initially, which can cause dehydration. This can affect digestion by inhibiting proper nutrient absorption and leading to constipation. It is crucial for those on a keto diet to consume adequate fluids to support their overall health. Besides plain water, herbal teas or broth can also contribute to hydration while providing additional nutrients. Moreover, ensuring adequate potassium and magnesium intake can assist with staying hydrated, particularly vital electrolytes often lost during the keto transition. Electrolytes support numerous body functions, including muscle contraction and nerve function, which can be impacted during dietary changes. In conclusion, while a keto diet can offer many benefits, adequate hydration, balanced nutrition, and potentially supportive probiotics are fundamental to sustaining gut health.
Conclusion: Prioritizing Gut Health on Keto
In summary, the relationship between gut health and the keto diet is multifaceted. While some benefits exist, including potential positive shifts in gut microbiota, challenges also arise related to fiber intake and digestion. Maintaining a balanced approach that emphasizes whole, high-fiber foods within the diet is essential for preserving gut health while enjoying the benefits of a ketogenic lifestyle. Paying attention to bodily responses while experimenting with different food choices can help individuals navigate the complexities of the keto diet successfully. Those interested in making dietary changes should always consider consulting healthcare professionals for personalized advice, especially regarding gut health matters, which can greatly vary among individuals. Additionally, enhancing gut health can improve not just digestional aspect but overall quality of life. Personalization, hydration, and smart nutritional choices must remain at the forefront when adopting a keto diet. By thoughtfully crafting a keto plan that prioritizes these factors, one can achieve not only weight loss goals but also enhanced gut health.
This is another paragraph with exactly 190 words…