Aerobic Exercise Benefits for Individuals with Different Diabetes Types
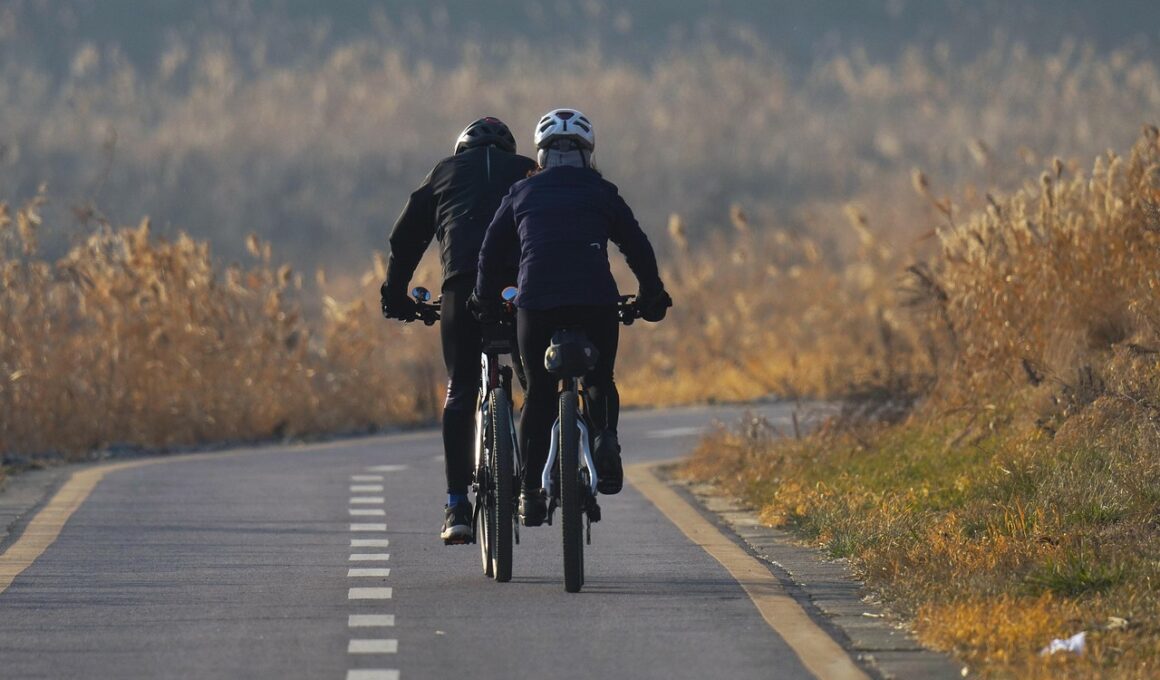
Aerobic exercise plays a pivotal role in managing diabetes effectively. It helps control blood sugar levels, which is crucial for individuals diagnosed with diabetes. Regular aerobic physical activity, such as walking, jogging, cycling, or swimming, can improve cardiovascular health. This improvement significantly reduces complications associated with diabetes. Engaging in aerobic exercises consistently allows diabetic patients to increase their insulin sensitivity, making it easier for the body to regulate blood glucose levels. Additionally, aerobic exercises promote weight loss, which is beneficial for individuals suffering from type 2 diabetes. Exercise can help reduce fat accumulation and improve the body’s overall metabolism. Furthermore, aerobic activity elevates mood and reduces stress, two factors that can contribute to unhealthy eating habits or sedentary behaviors. Types of aerobic activities can vary in intensity, allowing individuals to choose what best suits their fitness levels and preferences. Personalized plans should consider potential complications throughout the exercise journey, ensuring good practices for safety and effectiveness. Patients should consult with healthcare professionals before starting any new exercise regime to tailor programs according to their specific conditions.
Understanding the Different Types of Diabetes
Diabetes is primarily categorized into two main types: Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes. Type 1 diabetes occurs when the body fails to produce insulin, a hormone crucial for converting glucose into energy. It is often diagnosed in children and young adults. On the other hand, Type 2 diabetes typically develops when the body becomes resistant to insulin or does not produce adequate amounts. This type is more common in adults and is often linked to obesity and inactivity. Both types can significantly benefit from regular aerobic exercise. People with Type 1 diabetes must monitor their blood sugar levels closely, especially during and after workouts. They may require additional carbohydrates to offset the impacts of exercise on insulin. In contrast, individuals with Type 2 diabetes may find that aerobic workouts help in managing their glucose levels effectively. Aerobic exercise not only lowers blood sugar levels but also helps prevent further complications like heart disease, a common risk for anyone with diabetes. Understanding the differences in how exercise impacts both types of diabetes is crucial for effective management and improved health outcomes for those affected.
Research indicates that aerobic exercise can significantly mitigate the effects of diabetes-related complications. Regular participation in aerobic activities often results in increased lung capacity, which is beneficial for overall fitness. Individuals suffering from diabetes may experience improved circulation and reduced levels of triglycerides and cholesterol. Lowering these can significantly reduce the risk of cardiovascular problems, a major health concern for diabetic individuals. Furthermore, studies have shown that aerobic exercise enhances psychological well-being. This aspect is especially critical for those living with diabetes, as emotional distress can lead to detrimental health choices. Additionally, structured aerobic workouts offer increased energy levels, promoting overall physical activity. It can be easy to overlook a sedentary lifestyle, but introducing aerobic exercises can be a step toward a healthier lifestyle. Balancing exercise with proper nutrition and regular monitoring of glucose levels ensures a comprehensive approach to managing diabetes. Consequently, it is essential for diabetic individuals to engage in aerobic exercises frequently. By making this a part of their regular routine, they can experience lasting benefits that enhance both their physical and emotional health, ultimately leading to a higher quality of life.
Notably, tailored aerobic exercise programs are essential for maximizing their effectiveness for individuals with diabetes. Each person’s fitness levels, diabetes management requirements, and preferences vary. Therefore, involving healthcare professionals in the design of an exercise regime can lead to better outcomes. Programs should incorporate both moderate- and high-intensity workouts suitable for the individual’s current health status. Moderate aerobic activities generally include walking briskly or cycling at a leisurely pace, while high-intensity sessions may encompass jogging or circuit training. The choice of exercise should promote enjoyment, thereby encouraging consistency. Regular engagement in these activities helps build resilience, and the body’s adaptation patterns can further enhance insulin sensitivity over time. Another important aspect is hydration during aerobic activities, particularly for diabetes patients. Adequate fluid intake can help prevent dehydration, and it responsible for maintaining stable blood glucose levels during and after exercise. It is crucial to monitor one’s body responses, adjusting the activities as necessary to avoid any adverse effects. As patients get more comfortable with their routines, they may look to increase intensity or duration, further optimizing their exercise benefits for future health improvements.
The Impact of Aerobic Exercise on Weight Management
Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight is especially vital for individuals diagnosed with Type 2 diabetes. Aerobic exercise contributes substantially to weight loss, supporting diabetes management goals. Engaging in aerobic activities can burn significant calories, which aids in creating a caloric deficit necessary for weight reduction. Moreover, exercising can promote fat loss while preserving lean muscle mass, which plays a crucial role in maintaining a healthy metabolism. When paired with good nutrition, regular aerobic workouts are effective strategy in the battle against obesity. Moreover, patients can discover that increased physical activity contributes to improved self-esteem and confidence. Boosting emotional and psychological well-being can have a direct influence on adhering to a healthier lifestyle. Furthermore, weight loss has been linked to improved blood sugar control, presenting a powerful incentive to stay active. Various activities can be tailored to individual preferences, helping them choose engaging exercises. A sustainable workout regimen can be established, leading to lasting weight control and better management of diabetes. Furthermore, the social aspect of group exercises can create accountability and encouragement, which can be an essential factor in achieving long-term fitness goals and maintaining motivation.
Combining Aerobic Exercise with Dietary Changes
Aside from regular aerobic exercise, dietary changes must also be made to achieve an overall management of diabetes. Integrating a balanced diet rich in fiber, lean proteins, and healthy fats complements the effects of aerobic workouts. It is essential to comprehend how food choices can impact blood sugar levels. Consistent meal timing along with exercise can contribute to more stable glucose levels. Patients are encouraged to limit their intake of processed sugars and carbohydrates, which can lead to spikes in blood sugar. Maintaining a food diary can help monitor dietary habits and understand patterns that impact glucose levels. Furthermore, hydration remains important, especially when participating in aerobic activities. Drinking adequate water can facilitate better performance, especially during intense physical activities. Additionally, combining aerobic exercise with resistance training can enhance overall fitness and contribute to improved glucose management. Developing a comprehensive approach that aligns exercise and nutrition can cultivate long-term health benefits. This synergy can positively influence how individuals with diabetes manage their condition, leading to improved quality of life and reducing the risk of complications in the long run.
Lastly, support and community resources can play a significant role in encouraging diabetic individuals to adopt aerobic exercise into their routines. Joining local fitness groups or diabetes support organizations can provide motivation and accountability. Sharing personal experiences and challenges can foster a supportive environment where individuals feel comfortable discussing their obstacles. Moreover, engaging with a coach or personal trainer who specializes in diabetes management can provide additional guidance. These professionals can help create individualized fitness plans suited to specific needs and goals. Participating in community events such as charity walks or health fairs can also enhance motivation and promote a sense of belonging. The journey toward better health can sometimes feel isolating; therefore, integrating a community aspect can significantly enhance the experience. Overall, maintaining a proactive approach to managing diabetes through consistent aerobic exercise, proper nutrition, and support systems can lead to significant improvements in both physical and mental health. As individuals learn to embrace an active lifestyle, they can gain confidence in their ability to manage diabetes effectively, significantly enhancing their quality of life.