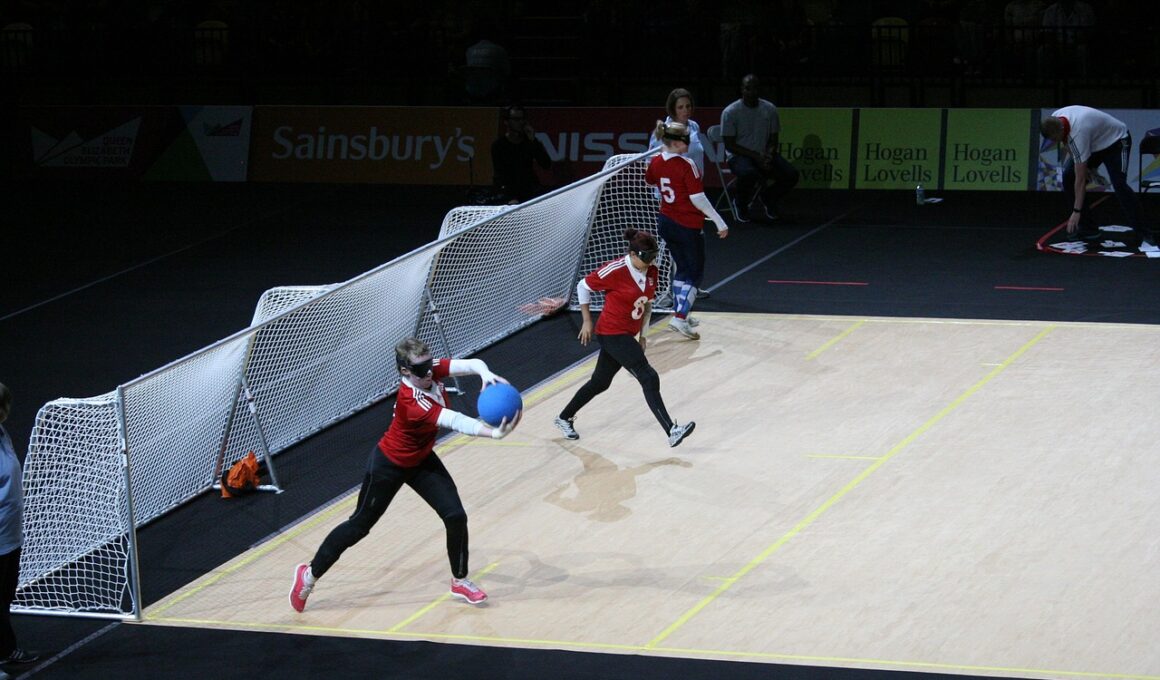
Future Trends and Research in Adaptive Blind Soccer
The development of blind soccer has engaged the attention of athletes, coaches, and researchers alike. As adaptive sports receive increased focus, the need for tailored methodologies becomes imperative. Future trends suggest innovative approaches to enhance engagement for visually impaired players. Research is essential for identifying the best practices regarding physical training and mental preparedness. Incorporation of technology, such as sound-producing balls and wearable sensors, will fundamentally alter training methods. These advancements promise to revolutionize skill acquisition and performance analysis. There is a significant emphasis on sensory integration, enabling athletes to navigate the field more effectively. Coaches must not only understand the strategies of the game but also cater to sensory learning. Engaging the community to support blind soccer programs will become pivotal in the coming years. Partnerships with schools and local sports organizations may foster growth and development. Creating inclusive environments will help build passionate players. Thus, adaptation and innovation are vital for the future of adaptive blind soccer. By prioritizing these aspects, individuals will have the opportunity to thrive in competitive settings.
With advances in coaching methodologies, training sessions for blind soccer will see enhancements that emphasize inclusion and skill development. Coaches will be required to adapt their training approaches, focusing on auditory signals that guide the players. Understanding the best ways to communicate these auditory cues will be a critical area of research. Beyond merely enhancing performance, it is also essential to consider psychological aspects. The mental toughness of athletes needs to be cultivated. Innovations like virtual reality simulations may support mental training by mimicking game scenarios without physical constraints. Furthermore, peer mentoring programs can create supportive networks, allowing more seasoned athletes to guide newcomers. These programs can accentuate both skill acquisition and emotional resilience. By fostering collaboration among athletes, this enhances community building and promotes the sport. Looking ahead, development programs should target increasing access to adaptive training resources. This includes specialist equipment and structured competition opportunities. Continuous research into best practices will further refine coaching strategies and game techniques. The future promises evolving dynamics that not only enhance athletic capabilities but also build confidence among participants, empowering them through the sport.
Technology’s Role in Blind Soccer
Technology will play an increasingly influential role in shaping the future of adaptive blind soccer. The integration of auditory and tactile technologies can enhance the gameplay experience dramatically. Sound-emitting soccer balls allow players to use their hearing to detect the ball’s location, proving critical in developing spatial awareness. Additionally, mobile applications may assist in tracking player performance and progress. By analyzing data gathered through these platforms, coaches can create personalized training plans. Advanced wearables can provide real-time feedback through auditory cues, helping athletes refine techniques on the field. Blind soccer’s accessibility can benefit from these partnerships with technology firms dedicated to inclusivity. Collaboration will be vital in developing innovative solutions tailored for athletes with visual impairments. Furthermore, research into augmented reality may allow training simulations that refine skills in lower-pressure environments. This can lead to improved readiness for real-match conditions. Future technological advancements will not only impact how training sessions are structured but can also enhance the spectacle of competitions. Increasing audiences can interact with such innovations, thereby broadening the sport’s reach and appeal. Emphasizing these technologies holds immense potential for elevating adaptive blind soccer as a discipline.
The role of community engagement cannot be overstated in the ongoing development of blind soccer programs. Creating grassroots initiatives is essential for sustaining interest and enthusiasm among players, families, and volunteers. Community events and fundraising campaigns can specifically cultivate awareness and support for adaptive sports. Schools and other institutions can play a major part in this process, integrating blind soccer into their physical education programs. By involving local businesses as sponsors, more resources can be allocated toward equipment and training. Collaboration between organizations dedicated to adaptive sports will also enhance recruitment and retention efforts. Regular competitions can help build camaraderie among participants, providing invaluable social interaction. Additionally, community engagement can extend to inclusivity efforts for transitioning athletes into mainstream sports. Ultimately, these programs should embrace diversity and promote equal opportunities. Training for coaches within the community can enhance understanding of the emotional and physical needs of blind athletes. Symposiums and workshops can facilitate knowledge sharing among professionals. Research in this area can identify sustainable practices that will contribute to the long-term viability of blind soccer. Active participation helps foster a sense of belonging for athletes, establishing a foundation for the sport’s growth.
Sustainability and Growth of Adaptive Blind Soccer
To ensure sustainability in adaptive blind soccer, establishing solid frameworks for long-term growth is crucial. In addition, financial backing will foster the expansion needs of teams and programs. Innovative fundraising strategies, collaborating with local businesses, and leveraging social media will be essential to attract funds. These resources will assist in providing specialized equipment, such as customized soccer balls and training gear. Legislation advocating for adaptive sports can further support these initiatives, ensuring that programs receive appropriate government recognition. This may pave the way for more inclusive opportunities and encourage broader participation. Furthermore, establishing partnerships with colleges can create pathways for young athletes to continue pursuing the sport competitively. Creating university teams focused on blind soccer can generate new talent pools and enhance the competition level. Another essential factor is fostering skill development and mentorship opportunities for players. Additionally, competitive leagues should be developed to recognize achievements at multiple levels, instilling pride in participants and communities. Continuous assessment and research into best practices can identify emerging talent and address barriers. Building a legacy will revolve around sustaining community focus and encouraging continuous participation in adaptive blind soccer.
Inclusion of mental health resources in adaptive blind soccer is essential, contributing to holistic athlete development. Integrative approaches that incorporate sports psychology can empower visually impaired athletes. Access to counselling services that address stress and anxiety associated with competition can significantly improve overall player wellness. Mental resilience training is crucial, as it builds coping mechanisms for challenges both on and off the field. Research focusing on these areas can inform coaching practices and support programs tailored for blind athletes. Furthermore, creating workshops that educate coaches about mental health considerations will be pivotal. By creating understanding, coaches can better support their athletes’ emotional wellbeing. Peer support groups can also foster an encouraging environment, promoting open dialogues about experiences and challenges. Additionally, introducing mindfulness practices may aid athletes in managing performance pressure. As adaptive blind soccer grows, strategies surrounding mental wellness must evolve simultaneously. Balancing physical training with mental conditioning will prepare athletes for peak performance. Sustainability of the sport will become directly linked to the mental and emotional well-being of its participants. This dual focus on physical and mental health can ensure holistic development within competitive frameworks.
Conclusion: The Future of Adaptive Blind Soccer
The future of adaptive blind soccer is bright, promising new avenues for engagement, performance, and community involvement. Through continuous research and innovation, tailored resources can emerge that enhance the athlete experience. Anticipated developments in technology will facilitate both training and gameplay, making the sport increasingly appealing to newcomers. Involvement from various sectors will help create inclusive environments that are accessible for all. Increased sustainability through community engagement will further foster the growth of blind soccer programs. The importance of mental health resources cannot be overlooked, as this holistic approach will empower players both mentally and emotionally. These considerations not only impact individual athletes but also enhance the efficacy of teams across various levels. Collaboration among adaptive sports organizations will drive shared initiatives aimed at expanding opportunities for participation and competition. The culmination of these efforts leads to a more inclusive sporting landscape where dynamic blind soccer thrives. This pioneering spirit will be essential as adaptive blind soccer continues to evolve, inviting further research and dedication from all stakeholders. Ultimately, the trajectory of this sport holds the promise of significant advancements, contributing positively to the lives of countless athletes.
As we move forward, it is essential to seek ongoing support to ensure that adaptive blind soccer continues to flourish. Encouraging investment in this sport can lead to improved facilities, training capabilities, and resources for athletes. By actively promoting awareness and understanding of the unique challenges faced by visually impaired individuals, community-driven initiatives can foster strong participation rates. Engaging with both local and national governing bodies will advocate for policy changes that facilitate opportunities in adaptive sports. The broadening of perceptions regarding adaptive sports will encourage the inclusion of blind soccer in educational settings and institutional programs. Community awareness campaigns can shed light on upcoming events, inspiring more individuals to take part. Encouraging participation from diverse groups will enrich the experience for everyone involved. With a concerted focus on creating supportive networks, the future of adaptive blind soccer thrives on inclusivity and empowerment. As interest surges, various stakeholders must join forces to nurture and grow the sport. The vision should encompass equal access and opportunities for athletes, culminating in vibrant communities united through blind soccer. Through unity and shared passion, the sport will pave pathways to growth and transformation for future participants.