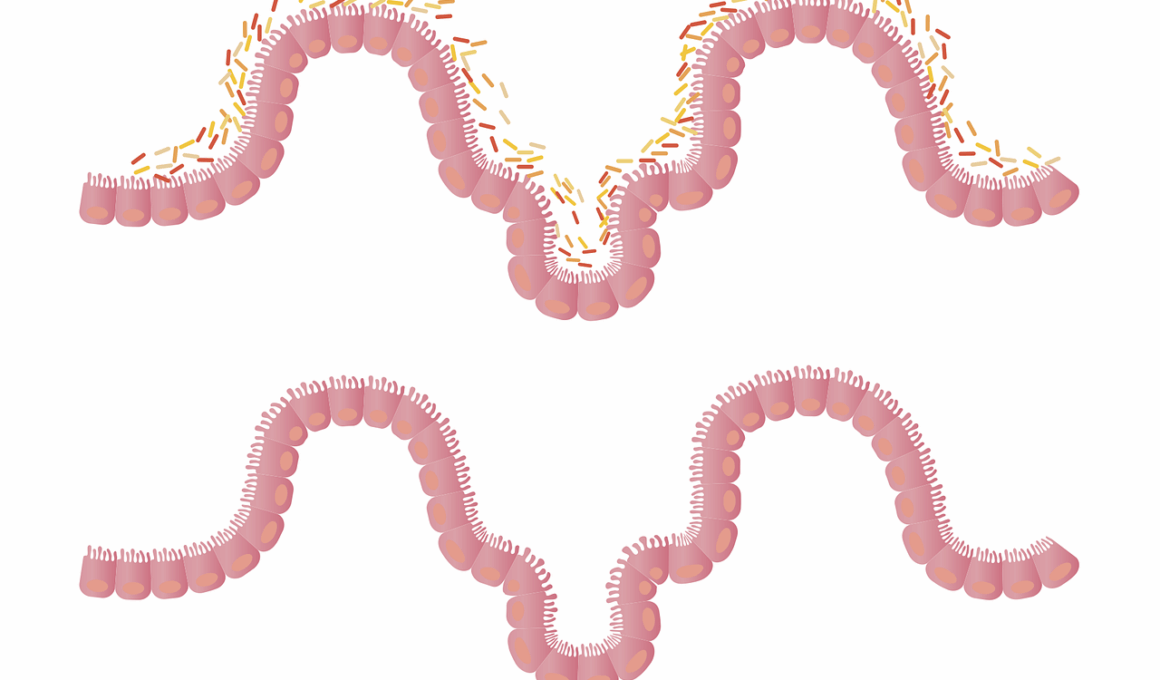
Gut Health and Its Influence on Athletic Recovery
Athletic performance and recovery are closely linked to gut health, as the gut microbiome plays a crucial role in immune function, inflammation, and nutrient absorption. Athletes often engage in rigorous training, leading to increased stress on their bodies. This stress can modify gut bacteria, negatively influencing overall health. A healthy gut microbiome supports recovery by enhancing digestion and reducing inflammation. Foods rich in probiotics, such as yogurt and fermented products, promote the growth of beneficial bacteria. These bacteria can aid in breaking down food, improving nutrient availability, and supporting immune health. Furthermore, consuming adequate fiber is essential for feeding these beneficial bacteria, ensuring a balanced microbiome. Incorporating prebiotics, found in foods like bananas and oats, can bolster gut health. Additionally, hydration is critical; dehydration can disrupt gut function, causing increased fatigue and slower recovery. Overall, focusing on gut health through a nutritious diet is advantageous for athletes aiming to optimize their recovery and performance. In the competitive world of sports, every edge counts, and understanding gut health’s role is becoming increasingly significant for every athlete’s success.
The gut microbiome’s composition varies among individuals and can significantly influence athletic performance and recovery. Research highlights that athletes possess different gut microbiomes compared to sedentary individuals, demonstrating a diverse and beneficial population of bacteria. This diversity is critical for optimal metabolic function and recovery after intense physical exertion. For athletes, implementing dietary strategies that enrich gut microbiota may involve consuming varied and nutrient-dense foods. These foods include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, and seeds, each providing essential vitamins and minerals that support microbial balance. Supplementing with probiotics may further enhance this diversity, helping to combat exercise-induced stress on the gastrointestinal tract. In addition, athletes should monitor food sensitivities, as these can disrupt gut health. Evaluating which foods promote individual well-being and enhance recovery is vital. Personalization of diet enables athletes to identify optimal nutritional strategies. Moreover, understanding interactions between gut health and stress can lead to better recovery. Stressful exercise sessions can harm gut bacteria, leading to potential complications. Thus, addressing these factors through healthy eating habits can create a rich foundation for recovery, allowing athletes to reach their highest potential.
The Role of Hydration in Gut Health
Hydration is essential for gut health; adequate fluid intake supports the digestive process and the functionality of gut bacteria. When athletes become dehydrated, intestinal permeability often increases, leading to a condition commonly referred to as ‘leaky gut’. This condition can provoke systemic inflammation and impact recovery negatively. Drinking water, alongside electrolytes, is crucial for clearing toxins and ensuring optimal gastrointestinal function. Athletes engaging in vigorous exercise should pay attention to hydration before, during, and after training. Consuming fluids that contain electrolytes can help maintain hydration levels and support gut integrity. Additionally, research shows that hydration levels affect the composition of gut microbes, indicating that maintaining proper fluid levels can further promote a healthy microbiome. Incorporating hydrating foods such as cucumbers, watermelon, and oranges can aid in both hydration and nutrient intake. By proactively managing hydration, athletes can significantly improve their gut health. This health directly contributes to enhanced recovery times, ultimately fostering a more efficient athletic performance during training and competition. Consequently, athletes who recognize the link between hydration and gut health may experience tangible benefits in their overall recovery strategies.
In addition to diet and hydration, the timing of nutrient intake also affects gut health and athletic recovery. Consuming meals and supplements strategically around workouts can enhance recovery and mitigate gastrointestinal distress. Post-exercise nutrition is particularly important for muscle recovery and glycogen replenishment, which are essential after intense training sessions. Athletes should focus on consuming balanced meals containing carbohydrates, proteins, and healthy fats within the recovery window. This combination ensures the body has essential nutrients to repair tissue and replenish energy stores effectively. Furthermore, athletes may also benefit from supplementation such as branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) and omega-3 fatty acids. These supplements can support recovery by reducing muscle soreness and inflammation. Digestion during post-exercise recovery can be enhanced by choosing easily digestible foods to minimize gastrointestinal discomfort. Observing how the body reacts to various intakes can guide athletes in fine-tuning their nutrition strategies for optimal recovery. Personal experimentation allows each athlete to create an individualized dietary plan that aligns with their preferences and needs, ultimately improving their performance potential. Hence, understanding the timing and composition of nutrient intake is crucial for effective recovery.
Impact of Stress on Gut Health
Stress plays a pivotal role in managing gut health, particularly for athletes facing high-pressure situations. The psychological strains of competition and intense training can harm the gut microbiome. Stress can decrease the diversity of gut bacteria, leading to negative health implications. A diminished microbiota may promote inflammation and affect recovery, causing higher susceptibility to illness or injury among athletes. As such, managing both physical and mental stress is paramount for optimizing gut health. Practicing stress-reduction techniques such as mindfulness, yoga, and deep-breathing exercises can mitigate these adverse effects. These techniques not only help improve mental clarity but also foster better gut function, which is essential during recovery. Athletes should recognize the importance of integrating relaxation techniques into their training regimen. Moreover, studies indicate that the gut-brain axis highlights the bidirectional communication between gut health and mental well-being. When this connection is nurtured, overall health can be enhanced. In this context, a holistic approach to recovery incorporates not only physical recovery strategies but also emotional and mental care, thereby promoting gut health. Thus, prioritizing mental health is an often-overlooked aspect of recovery strategies.
Athletes must consider the effects of nutrition on gut health, as the foods they consume directly impact both recovery and performance. Nutrient-deficient diets lacking in key vitamins and minerals can compromise gut integrity, hampering recovery post-event or training. Emphasizing a whole-food, nutrient-rich diet fosters overall gut health. Essential nutrients like zinc, vitamin D, and prebiotics support immune function and help maintain a healthy microbiome. Integrating these nutrients into every meal can bolster recovery and enhance performance over time. Furthermore, it is wise for athletes to avoid overly processed foods, which often contain additives and preservatives that negatively impact gut health. By prioritizing whole, unprocessed foods, athletes allow beneficial gut bacteria to thrive. This is particularly important since a thriving microbiome can provide the necessary support for muscle recovery and overall health. By conducting regular evaluations of their dietary preferences, athletes can identify and eliminate foods that may be detrimental to their gut health and performance. Monitoring how these foods influence recovery helps in creating an informed dietary approach toward becoming more resilient, allowing athletes to perform their best consistently.
Conclusion: Prioritizing Gut Health
In conclusion, understanding the significance of gut health is essential for athletes aiming to optimize recovery and improve performance. Strategies that promote a healthy gut microbiome include maintaining a balanced diet, ensuring proper hydration, and applying stress-management techniques. The intricate relationship between gut health and athletic recovery cannot be understated. Athletes benefit from a holistic approach to wellness that addresses nutritional intake, hydration needs, and mental well-being. Customizing diet and recovery strategies based on individual preferences enables athletes to create a sustainable approach to their health. This personalized care fosters resilient athletes capable of facing the demands of rigorous training and competition. Awareness of the food-gut connection should play an essential role in developing rigorous training regimens. Additionally, encouraging practices that maintain and enhance gut health leads to superior metabolic function, reduced inflammation, and decreased recovery time. As the field of sports science evolves, so too should athletes’ approaches to recovery and nutrition. Thus, they must integrate gut health strategies into their overall performance plan to achieve both immediate and long-term success in their athletic careers.
This article emphasizes the important intersection between gut health and athletic recovery, offering essential insights for athletes.